Are Digital Signatures Secure?
A digital signature is a type of electronic signature. A digital signature verifies the identity of the file owner by using a secure digital key to authenticate digital messages or documents.
When you need to create a digital signature, you will need a signing certificate, which verifies your identity and provides safe document authentication.
As a digital workflow solution, digital signatures enable users to sign documents from any location, at any time, offering businesses a competitive advantage and enhancing the customer experience.
When used appropriately, digital signatures can be even more secure than wet signatures when it comes to signing contracts, agreements, or any other sort of document.
So, just how safe are digital signatures? Is it possible to forge someone's digital signature?
Digital signatures are secure and impossible to forge. Because they are based on asymmetric cryptography, they have a private key that only the signatory knows and a public key that everyone can see; both are produced using a public key algorithm.
When the user wishes to sign a document, he uses his private key, which is unique and non-transferable; no one else has access to it.
To forge a digital signature, the attacker would need to get the signer's private key, which is extremely difficult.
However, if this occurs, the user can withdraw trust in the compromised key by using an alternative key that is in the hands of the Certification Authority (CA), which provides the certificates and stringent security procedures.
While digital signatures have been shown to be effective in securing online transactions, are they legal in Malaysia?
What Does the Law in Malaysia Say About Digitally Signed Documents?
The Digital Signature Act (DSA) 1997 governs digital signatures in Malaysia.
Digital signatures are defined by the DSA as "a transformation of a message using an asymmetric cryptosystem such that a person possessing the initial message and the signer's public key can accurately determine whether the transformation was created using the private key that corresponds to the signer's public key and whether the message has been altered since the transformation was made."
In Malaysia, a digitally signed document is recognized under the DSA if and only if the following conditions are met:
- The digital signature is validated by using the public key mentioned in a valid certificate issued by a recognized certifying body
- The signer attached that digital signature with the goal of signing the message
- The receiver has no information or notices that the signer has broken a duty as a subscriber, or the signer does not have the right to utilize the private key used to affix the digital signature
Now that you know that digital signatures are secure and legally binding in Malaysia, you may be wondering how the system works.
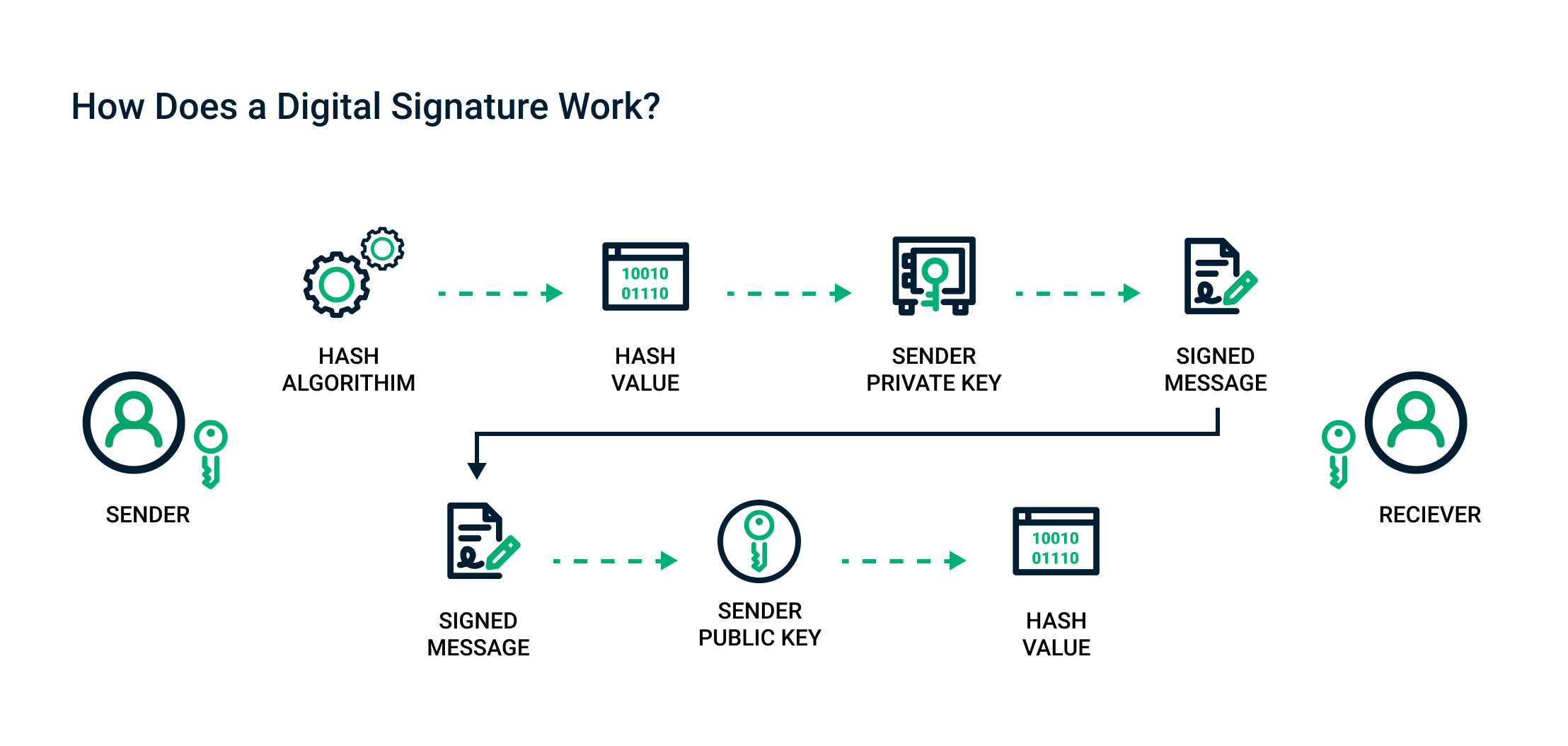
How Does a Digital Signature Work?
Digital signatures, as aforementioned, are based on digital certificates issued by certifying bodies (CA).
The certificates are used to link digital identities to a user's pair of keys and contain data such as their name, the date the certificate expires, a copy of the public key, and information about the CA that issued the certificate.
The corresponding CA checks each user's identity; once done, the user can create a digital certificate and sign whatever document they wish.
In turn, digital signatures are based on asymmetric cryptography and, as previously mentioned, have a public and a private key.
When you wish to sign a document, a hash (a unique and non-transferable identification of a digital document) is often created using a hash function. This hash is encrypted using the signer's private key and joined with the public key to form a digital signature.
In the same way, the receiver uses the public key to check the signature's identity. This ensures that the information sent between two people is not seen by anyone else.
All in All
Digital signatures are more difficult to forge than wet signatures because they employ electronic certificates and data encryption technologies to ensure that the digital signature cannot be modified.
Moreover, they provide a digital workflow solution that ensures business continuity even when partners are not present in the same room to sign paper documents.
News & Events
Keep up to date
- 18Dec
Ricoh recognised as a Top 5 global AV Integrator in SCN Top 50 Systems Integrators 2025
- 11Dec
Ricoh Recognised as a Sustainability Leader in Quocirca's 2025 Report
- 31Oct
Ricoh perovskite solar cells installed on Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency cargo transfer spacecraft1 HTV-X1
- 17Oct
Ricoh recognised among Forbes’ World’s Best Employers 2025
